Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Others | Additive manufacturing for spare parts in the rail industry Overview: One of the crucial topics for rail operators is maintenance and obsolescence management as rail vehicles can stay in service for over 30 years. Angel Trains identified additive manufacturing (AM), especially Stratasys’ FDM technology with the rail compliant Ultem™ 9085 resin filament, to be potentially beneficial on lead times as well as cost reduction for many spare part applications. Engineering & Consulting companies like DB ESG face new challenges coming along with the validation of these additively manufactured parts. Anisotropy in stiffness & failure due to the slicing strategy require new solutions as finite element simulations with traditional approaches lead to overly conservative designs. A combined effort of Stratasys, DB ESG, Angel Trains and Hexagon showed that Integrated Computational Materials Engineering (ICME) helps to tackle these issues on the application case of an armrest that was redesigned to be lighter and more cost-efficient while still fulfilling structural requirements. Solution: Digimat | 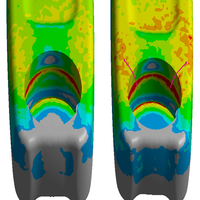  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:RadiciGroup Products:Digimat Industries:Material Suppliers | ICME for post-industrial and post-consumer recycled engineering polymers Overview: RadiciGroup High Performance Polymers is providing mechanically recycled engineering polymers. As developing recycled polymers for high-end applications is a challenge in and of itself, RadiciGroup High Performance Polymers turned to Hexagon’s Digimat and Marc to create an advanced predictive approach to provide customers the confidence these sustainable materials will meet their application requirements. RadiciGroup High Performance Polymers has validated three recycled products. One Post-Industrial Recycled (PIR) grade and two Post-Consumer Recycled (PCR) grades originating from airbag waste and from wheel cover waste. The impact of recycled engineering materials based on a Life Cycle Assessment is a CO2 reduction of an astonishing 84% to 88% compared to similar virgin materials. |   DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:SABIC Products:Digimat Industries:Medical Devices | Accurate prediction of part performance in response to static loads for short fiber reinforced composites - SABIC Overview: SABIC uses Digimat for high-fidelity anisotropic simulation, considering manufacturing effects and non-linear material behavior | 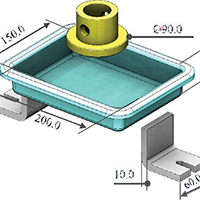  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Medical Devices | Anisotropic explicit simulation, considering manufacturing effects and nonlinearity - SABIC Overview: For short fiber reinforced composites, SABIC uses Digimat to define nonlinear strain rate dependent material model for accurate prediction of part performance under impact loads. | 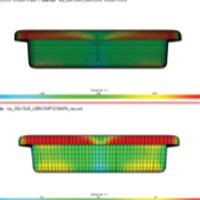  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Aerospace | Validating Digimat-VA from the coupon tests (NAL) Overview: Challenge: Characterization of CFRP using virtual allowable Solution: Multiscale non-linear VA simulation |  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Automotive | Influence of fibre orientation in the design of a collector box ground cable retention feature - INTEVA Challenge: Evaluate the strength of the retention feature during its assembly with the stator-can and satisfy the retention force requirement using Digimat coupled simulationsSolution: Anisotropic non-linear simulation, considering manufacturing effects and stiffness and strength predictions | 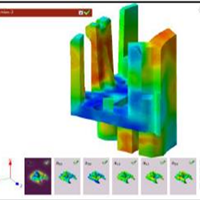  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Automotive | Fatigue lifetime prediction of short fiber reinforced plastics (SFRP) - DSM Overview: SFRPs are increasingly used, especially in the automotive industry. Metal replacement for assembly reduction and light weighting are the first drivers. But after having tackled the spatially varying stiffness and anisotropy and more recently the failure prediction, more advanced performances have to be addressed such as durability. |   DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Automotive | Database management for static and enhanced CAE analysis - RADICI GROUP Overview: Radici Group is an Italian privately held company acting worldwide in the chemical, synthetic fibers and engineering plastics sector. In the High Performance Polymer Division, they produce materials for engineering applications. CAE support is often required during this process, where it is crucial to generate and store simulated material cards in an easy to use and reliable manner. Digimat with its many tools not just offers a powerful solution for reverse engineering experimental data, but also makes that data easily accessible through its own database (Digimat-MX). Thanks to compatibility with all CAE simulation techniques commonly used in the industry, Digimat effectively gives Radici Group a way to handle all their activities within just one unified platform. | 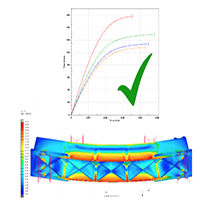  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Aerospace | Digimat allows to significantly decrease safety margins and reduce weight - SONACA | 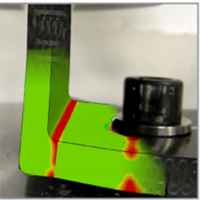  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Automotive | Simulating SMC part response with greater confidence using Digimat - Auto OEM Overview: While Sheet Molded Compound (SMC) materials have been widely used in the automotive industry for some time, recently there has been a move to apply SMCs on more structurally demanding components. Though the material has long been considered quasi-isotropic with relative success, it has become apparent in industry that due to the complex manufacturing process, optimal structural design is not possible without considering the real anisotropic nature of the material.. With growing demand from the market, now is the time to leverage advanced SMC modeling capabilities targeting crash performance. | 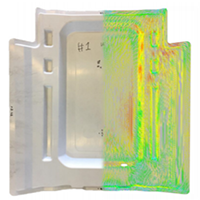  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Complete Solution to Accelerate the Design of Reinforced Plastic Parts Industries:Aerospace | Simulating effects of warpage in an additively manufactured composite layup tool - STRATASYS | 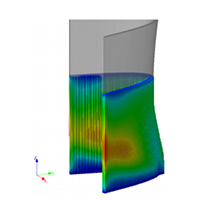  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Ford Motor Company Products:Complete Solution to Accelerate the Design of Reinforced Plastic Parts Industries:Automotive | Advanced anisotropic damping modeling for NVH optimization - FORD MOTOR COMPANY Overview: The Ford Motor Company uses glass fiber reinforced plastic materials for powertrain parts such as engine covers, air intakes and engine oil pans. These materials offer numerous benefits with regards to automotive component design including lightweighting and a better damping compared to metal. However, due to the complexities of the composite material microstructure which arise due to the manufacturing process, both the stiffness and damping of reinforced plastic materials are frequency dependent and locally anisotropic. The efficient design of such components from an NVH perspective requires the use of adapted techniques that can account for these specificities, from the material characterization stage up to the performance prediction of each design iteration. Challenge: The challenge can be framed as follows:
• How to build a material model capable of capturing the correct local anisotropic stiffness and damping behaviors
depending on the frequency and the local fiber orientation?
• How do the microstructure parameters influence the part’s NVH behavior?
The Ford Motor Company can see a great opportunity to employ this technique not only as a predictive simulation
methodology but also as a tool to fine-tune the parameters which drive a given part’s microstructure. This brings 2 benefits:
• The part’s NVH performance as well as weight will be optimized
• It reduces the need for corrective actions which typically increase component weight in order to meet acoustic targetsSolution: The technology developed by e-Xstream engineering in Digimat has been applied on 2 components:
•
An engine oil pan in order to:
- Apply the procedure to create a visco-elastic material model from DMA test data
- Demonstrate the accurate prediction of eigenfrequencies and acceleration peaks when applied on a FRF FEA compared to experiment.
•
An engine bracket in order to:
- Estimate the extent to which fiber orientation, fiber mass fraction and fiber length can influence a component’s NVH behavior
For each application, the fiber orientation distributions have been mapped onto the Nastran structural meshes. The effect of the manufacturing process on the prediction of the components behavior is taken into account via the mapped fiber orientations which have been associated with a multi-scale visco-elastic material model in FEA. For the engine bracket application, the mass fraction and the fiber length have been modified directly in the material file in order to gauge their influence on the simulation.Results Validation: The engine oil pan case study has demonstrated a significant improvement in how frequencies and acceleration peaks are identified compared to the usual isotropic method applied by Ford Motor Company: see Fig. 1
The engine bracket case study reveals that each microstructure parameter (the fiber orientation, the fiber length and the fiber mass fraction) has a significant potential influence on the component’s performance, enabling them to be considered as design parameters. Hence, by fine-tuning the material microstructure of the injected composite, a design engineer can optimize the component’s performance in terms of damping and lightweighting: see Fig. 2 |   DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat-RP Industries:Automotive | Digimat helps shortening the early design development cycle of an SFRP - SOKARIS | 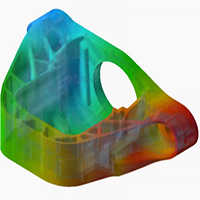  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat Industries:Aerospace | Computation of Allowable Values for CFRP - LEONARDO COMPANY |   DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
Company:Products:Digimat-RP Industries:Aerospace | Acoustic Simulation of Anisotropic Injection Moulded Parts - IPPS |  DOWNLOAD DOWNLOAD |
